Let’s learn the structure of the Italian present tense (it. il presente), its use and some important irregular verbs. You’ll also also some illustrated cards and exercises.
The three verb classes
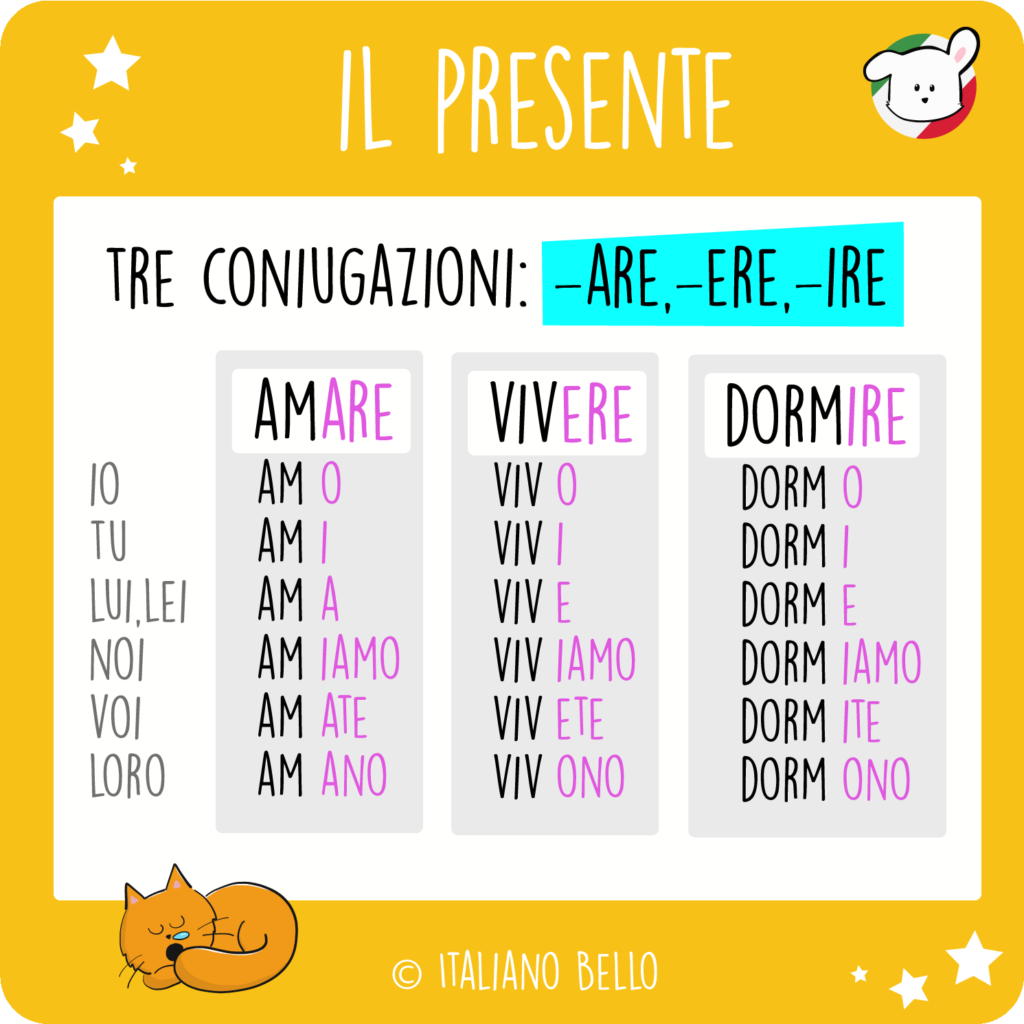
Before we talk about the present, we need to know that the verbs in Italian are divided into three verb classes. These are -are, -ere and -ire. These classes correspond to the ending of the infinitive form, so for example amare to love ends with –are, therefore it’s an –are verb. In order to conjugate the verb properly, you need to know to which class the verb belongs.
| –ARE | amare to love , giocare to play, mangiare to eat, lavorare to work, parlare to speak |
| –ERE | vivere to live, leggere to read, scrivere to write, prendere to take, conoscere to know |
| –IRE | partire to leave/depart, dormire to sleep, aprire to open, sentire to hear, offrire to offer |
The structure of the Italian present tense
To build the present tense you have to cut off the ending -are, -ere or -ire. Thus you get the so-called verb stem. Then you have to add the appropriate present tense ending. Each verb class has its own endings.
VERB STEM + PRESENT ENDING
| AMARE | VIVERE | DORMIRE | |
| io | amo | vivo | dormo |
| tu | ami | vivi | dormi |
| lui, lei | ama | vive | dorme |
| noi | amiamo | viviamo | dormiamo |
| voi | amate | vivete | dormite |
| loro | amano | vivono | dormono |
Essere e avere
Let’s review the conjugation of the most important Italian verbs: essere to be and avere to have.
| ESSERE | AVERE | |
| io | sono | ho |
| tu | sei | hai |
| lui, lei | è | ha |
| noi | siamo | abbiamo |
| voi | siete | avete |
| loro | sono | hanno |
Fare e andare
As for other the irregular verbs, the verbs fare to do / make and andare to go are very common and important to know.
| FARE | ANDARE | |
| io | faccio | vado |
| tu | fai | vai |
| lui, lei | fa | va |
| noi | facciamo | andiamo |
| voi | fate | andate |
| loro | fanno | vanno |
Preferire e capire
Some verbs of the -ire conjugation, like preferire to prefer and capire to understand, add -isc- between verb and ending (with exceptions of noi and voi) Look at the table and pay attention at the pronunciation (you find the audio at the beginning of this article)! Sadly, you cannot recognize if an -ire verb behave like this just by looking at it. Other common verbs like preferire and capire are finire to finish and pulire to clean.
| PREFERIRE | CAPIRE | |
| io | preferisco | capisco |
| tu | preferisci | capisci |
| lui, lei | preferisce | capisce |
| noi | preferiamo | capiamo |
| voi | preferite | capite |
| loro | preferiscono | capiscono |
Use
The Italian simple present is generally used to refer to current situations or states. To be more specific, the most commonly uses of the simple present are the following:
- Things that are generally true
| Il caffè è una bevanda. | Coffee is a drink. |
| L’italiano è una bella lingua. | Italian is a beautiful language. |
- General current situations
| Lavoro in un ufficio. | I work in an office. |
| Abito a Berlino. | I live in Berlin. |
- Habits
| Faccio colazione ogni mattina. | I have breakfast every morning. |
| Bevo spesso il caffè. | I often drink coffee. |
- Near future
| Domani lavoro tutto il giorno. | Tomorrow I’m working all day. |
| Sabato vado al cinema. | On Saturday I’m going to the cinema. |











One thought on “The Italian present tense”
preferisco il gelato al cioccolato